细胞周期
1.基本定义
Interphase:
- G1: cell growth
- S: DNA synthesis
- G2: fidelity check
Mitotic phase:
- Mitosis
- Prophase ——前期
- Prometaphase —— 前中期
- Metaphase —— 中期
- Anaphasel —— 后期
- Telophase —— 末期
- Cytokinesis —— 胞质分裂
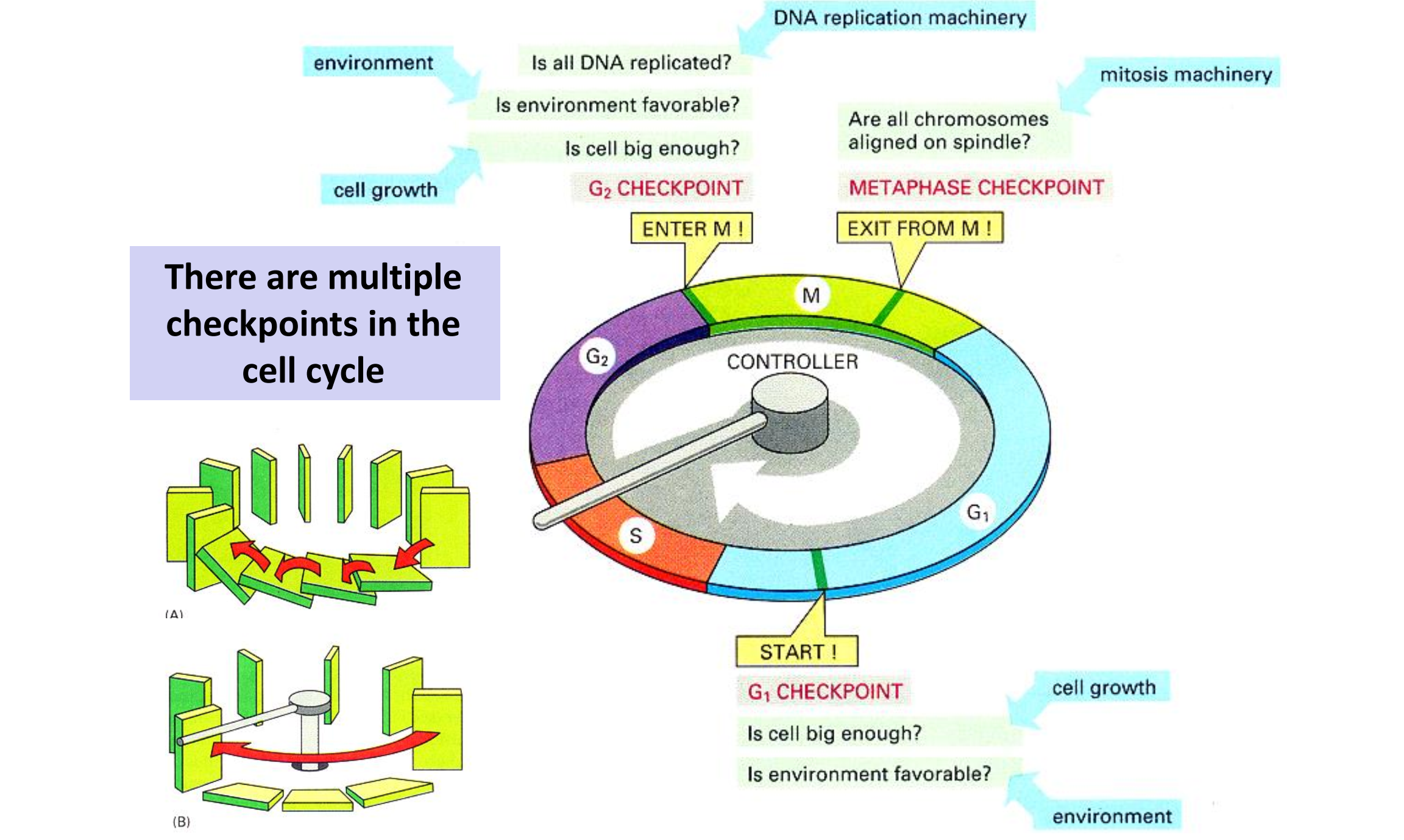
细胞必须对环境敏感,在适宜的条件下快速增殖,在恶劣的条件下保护自我。 细胞增殖必须足够准确,但不能完美。 如何保真?
- Perfection of machinery
- Quality control (checkpoint/检查点)
2.酵母细胞周期调控
- Yeast is an ideal model organism for cell cycle studies.
- Different yeasts have distinct cell cycle behaviors.
Cdc2 is an essential gene for fission yeast mitosis.
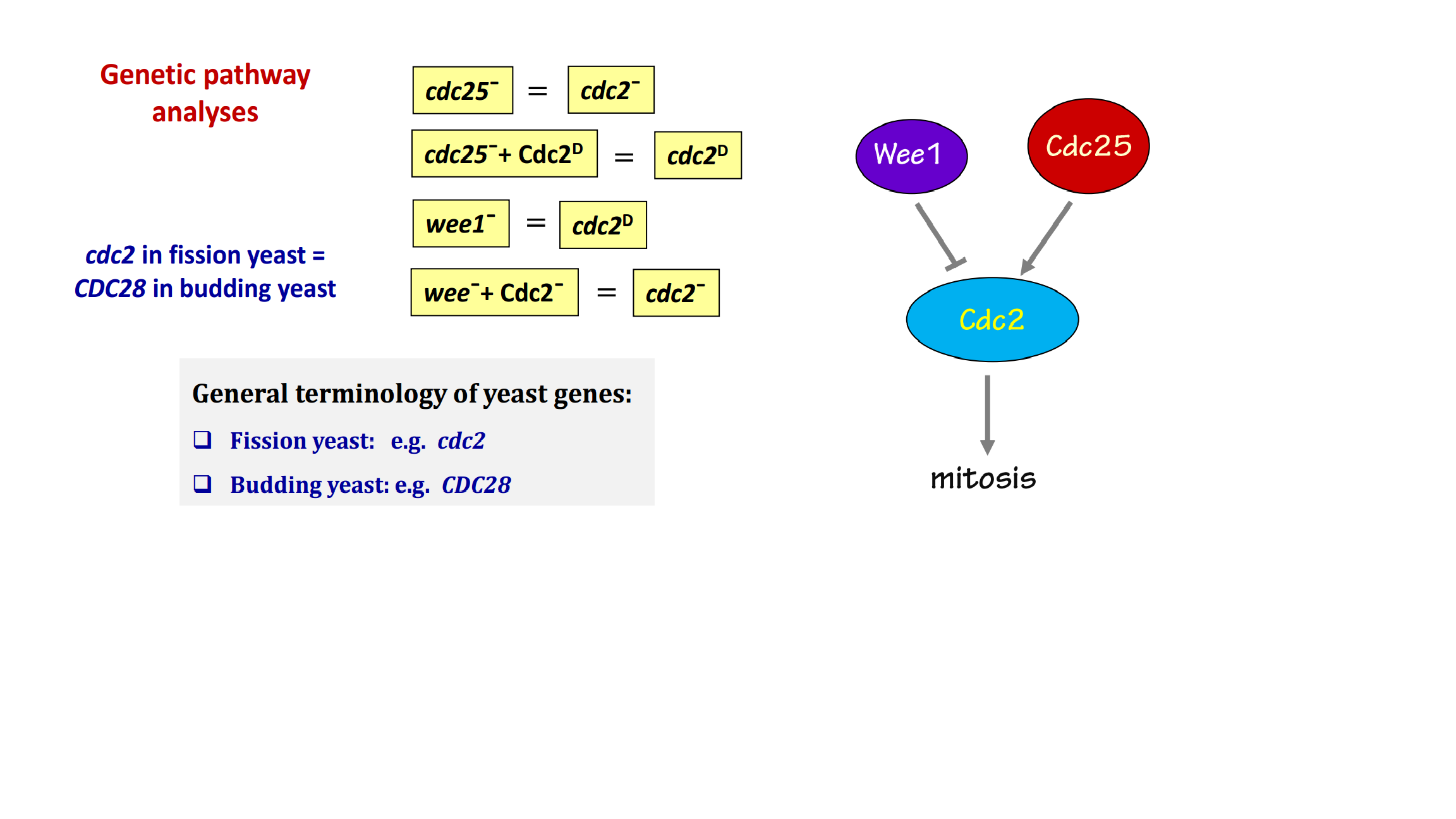 The fission yeast cell cycle is driven by Cdc2 activation cycle.
The fission yeast cell cycle is driven by Cdc2 activation cycle.
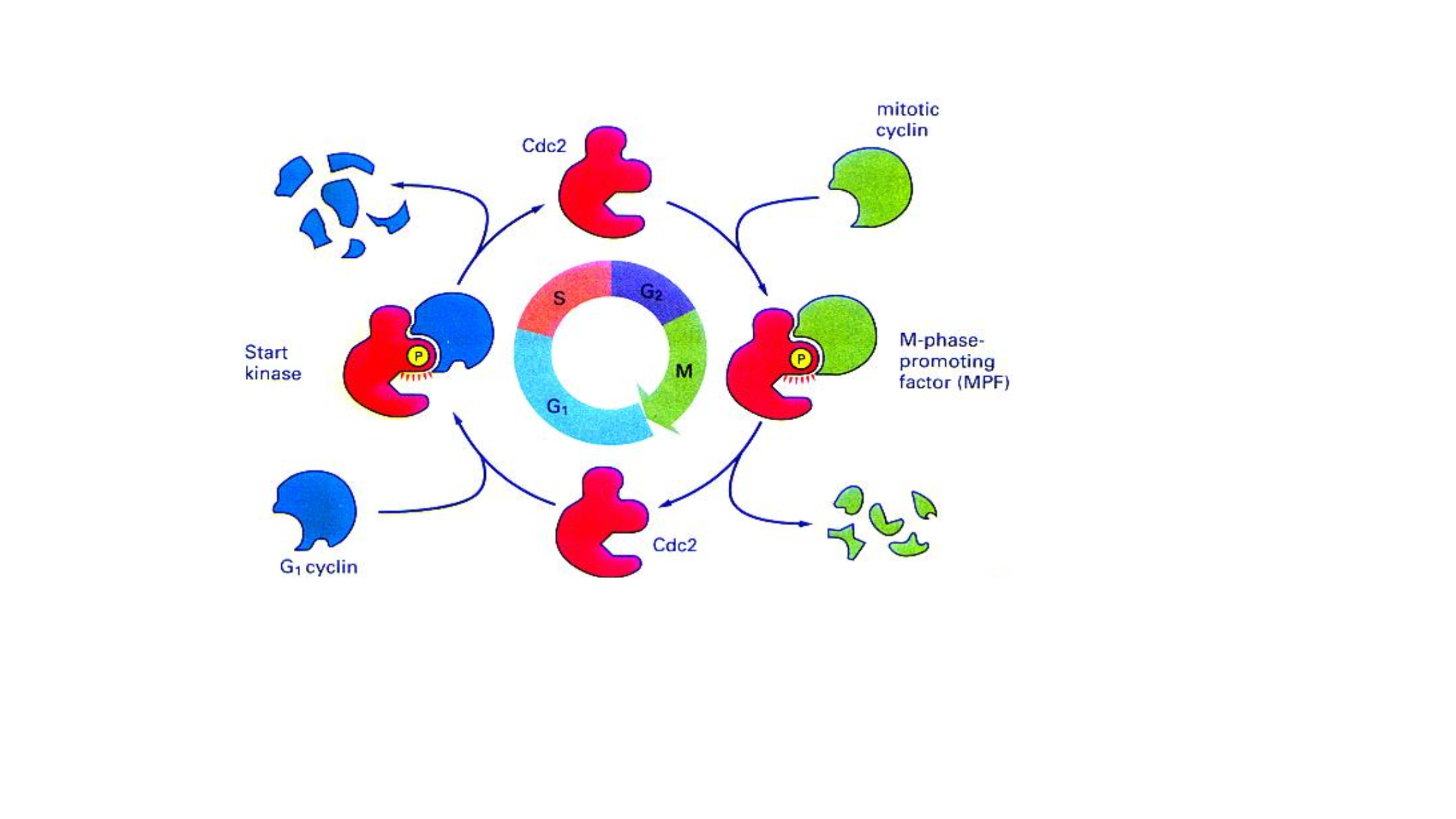 细胞周期是高度有序的。
细胞周期是高度有序的。
- Dependency of M on S phase:
- block S–> no M entry
- Dependency of S on M phase:
- block M–> no S entry
- Exceptions: Polytene chromosomes/多线染色体 (no M) Early embryogenesis/早期胚胎发生 (no G1)
3.高等生物细胞周期调控
高等动物细胞里面 Cdk1 = Cdc2
How can cyclin(细胞周期因子) levels fluctuate during the cell cycle?
Cyclins are subjected to
- stage-specific gene expression controls ,阶段特异性的基因表达。
- rapid protease-mediated degradation
Cdk inhibitors (Cki) add additional layer of regulations:
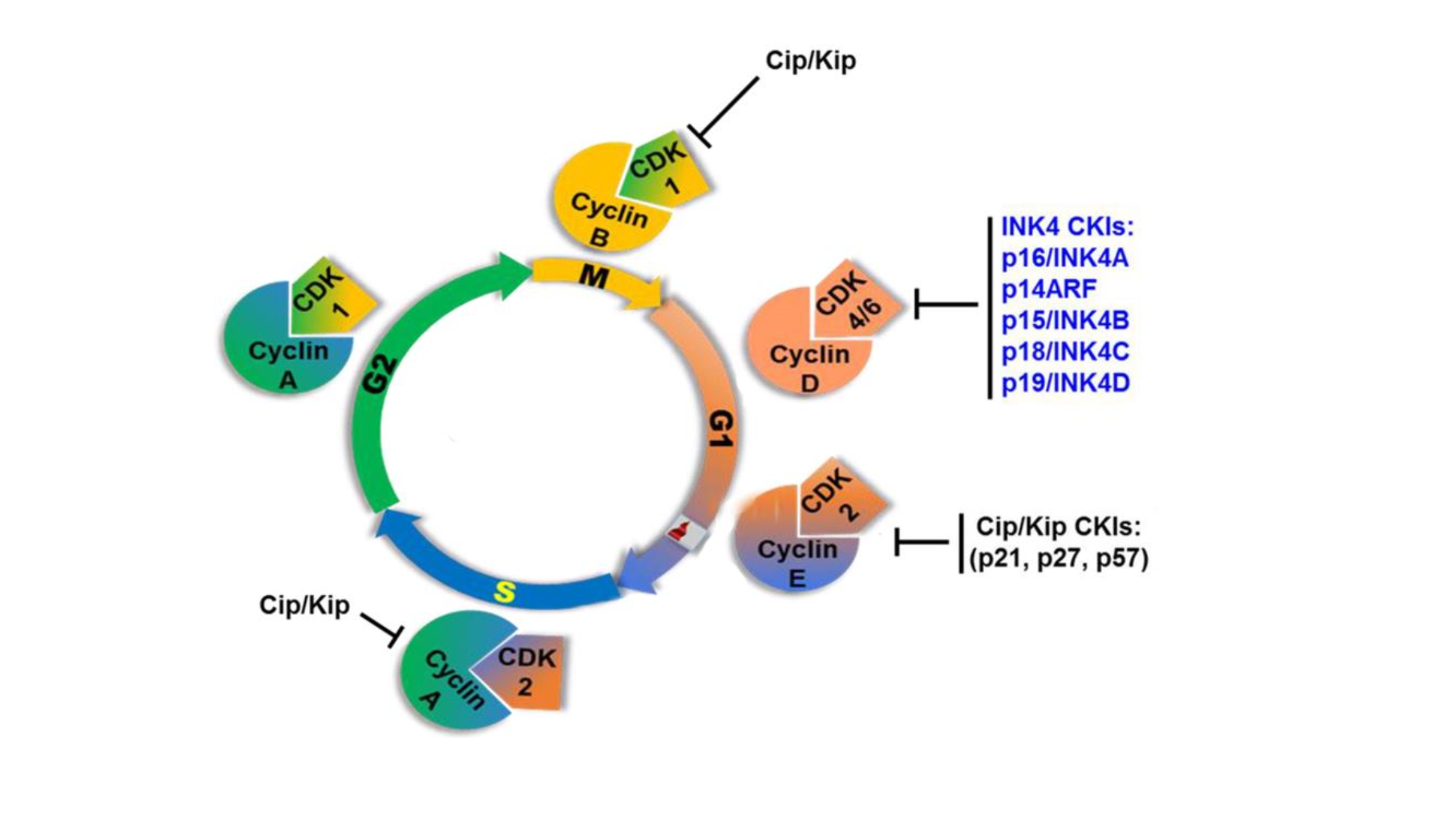
4.G1 –>S期
最主要的检查点是位于G1末期的 G1 checkpoint,在高等动物里面称为 Restriction point/R point。主要检查细胞的大小和周围的环境条件,决定细胞是否进入S期。
有多条信号通路调控G1期cdk的激活来调控细胞周期:
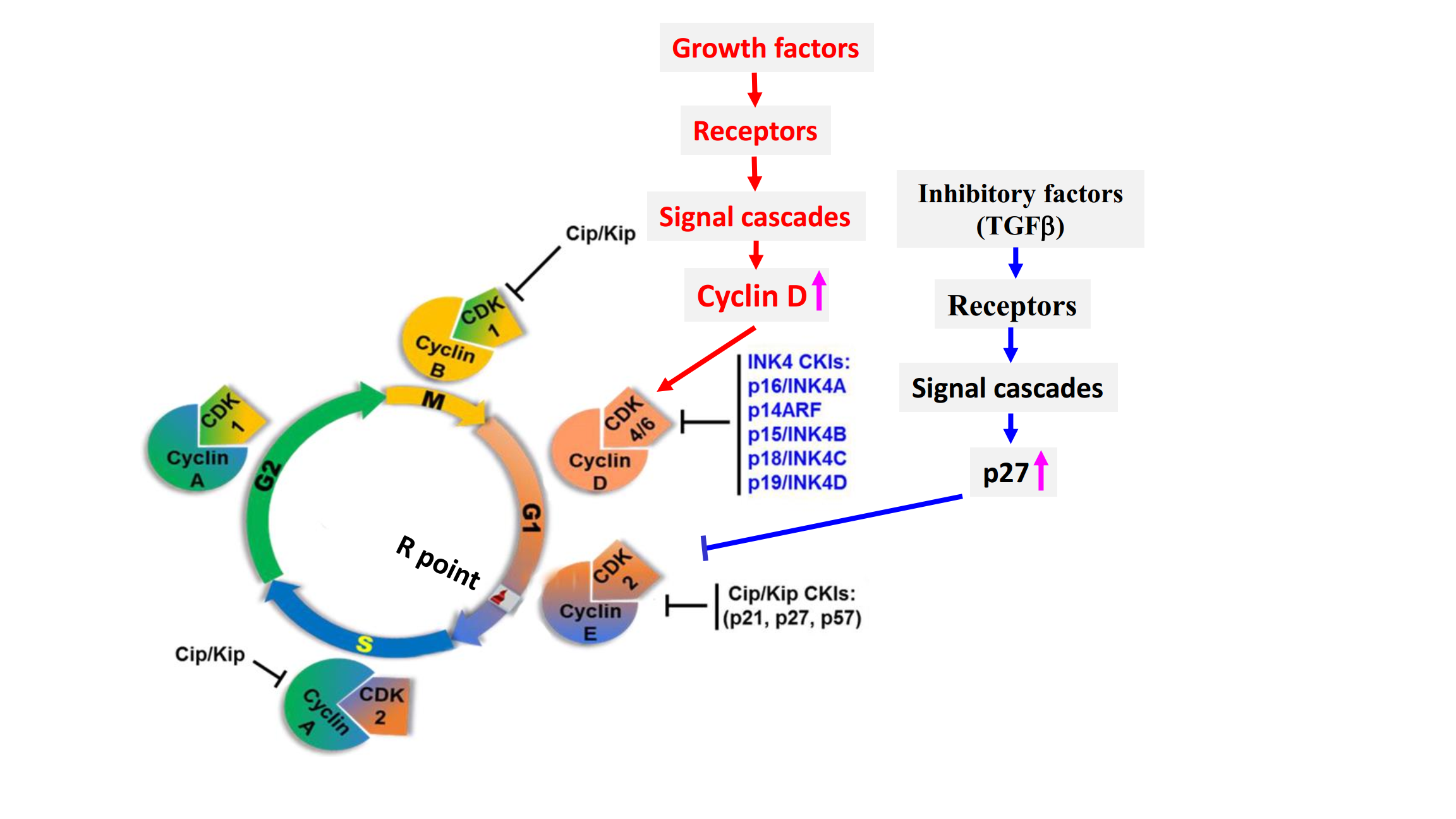
- The G1 checkpoint monitors cell size.
- The G1 checkpoint monitors fidelity of the genome.
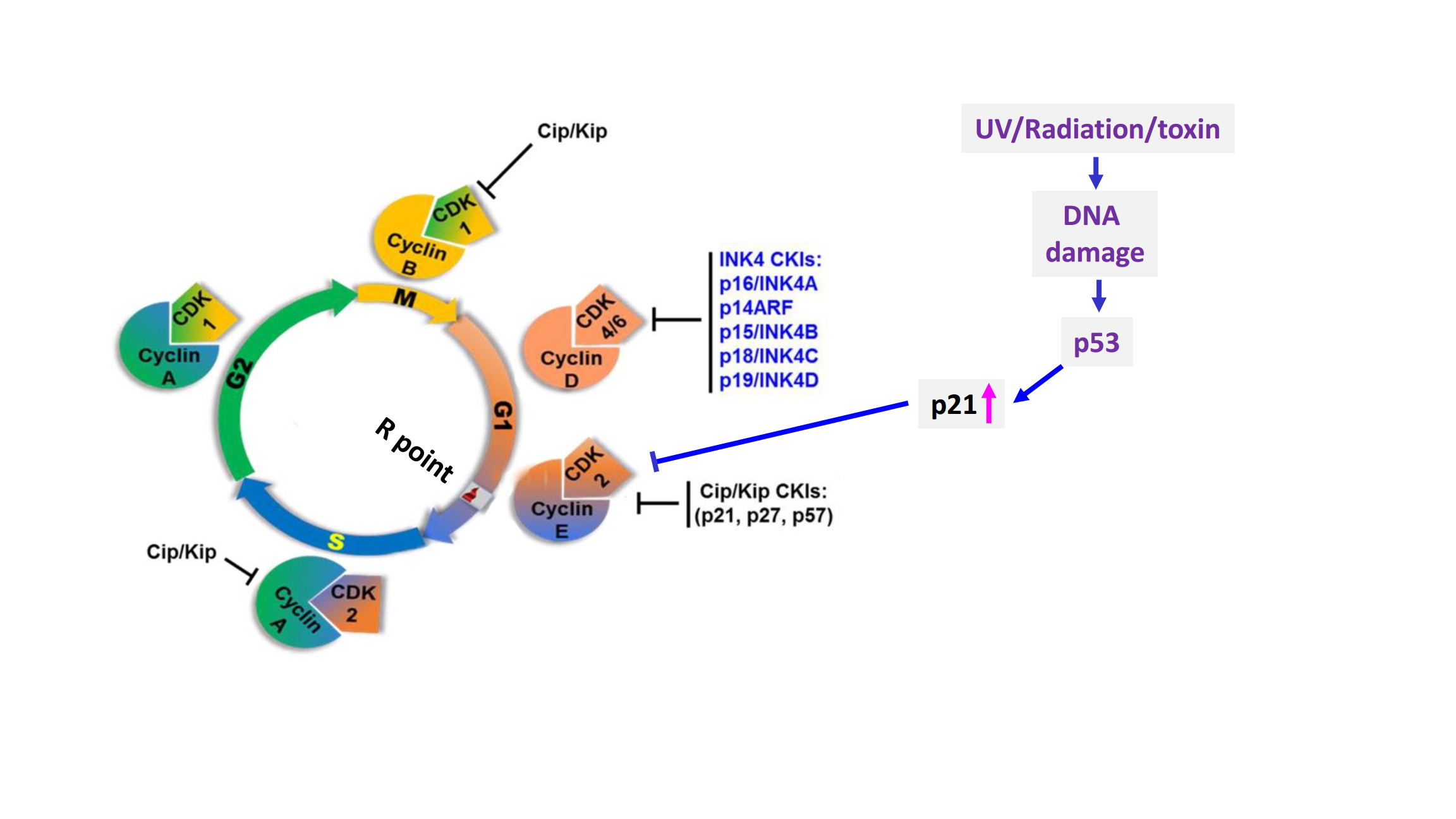
- p53是DNA损伤应答通路中的关键因子:
- P53是转录因子;
- P53是肿瘤抑制因子。–> Guardian of the genome!
3.What is the key Cdk substrate gatekeeping the R point?
Retinoblastoma protein (Rb) / 视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白
- Rb is a tumor suppressor gene!(肿瘤抑制基因).
- Rb在G1期末期被cdks 高度磷酸化。磷酸化的Rb才发挥功能。
- Tumor viruses inactivate Rb by neutralizing its activity!
- The TBD(T-binding domain of Rb) is critical for the tumor suppression function of Rb.
- The TBD might hold protein(s) critical for S phase progression.
- E2F / Rb-associated protein E2F regulates transcription of multiple genes important for S phase.
- DNA synthesis & chromatin assembly:TK,PCNA,histone H2A;
- cell cycle regulators:Cyclin A,E,D1,Rb,E2F1;
- Proto-oncogene MYC.
4.模式图(总结前面)
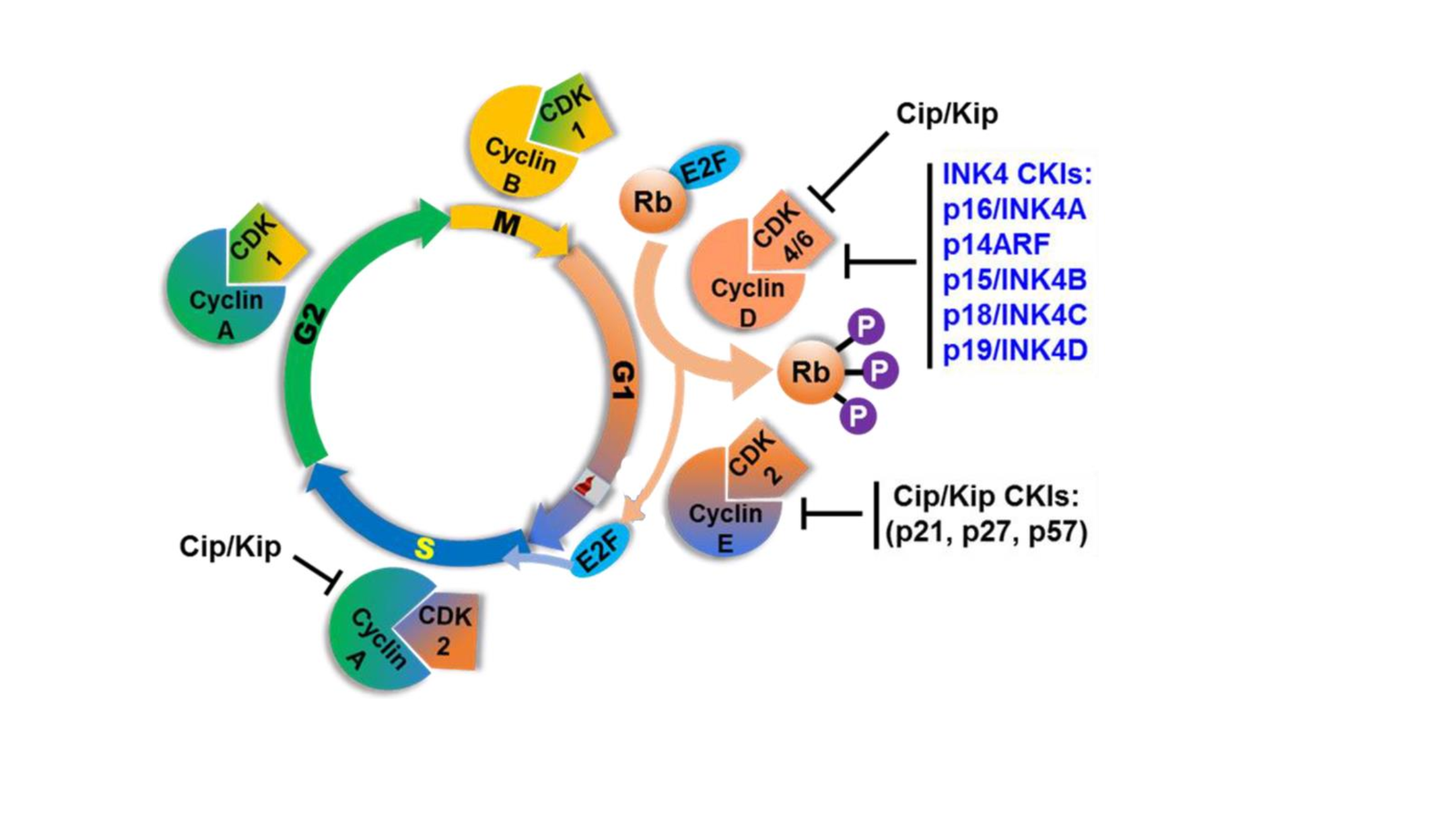
1.Rb binds to and prevents E2F from activation in early G1 phase! Rb在G1期早期与E2F结合,阻止E2F在早期的激活,在通过G1期的R point 之后发挥作用。
5.有丝分裂
5.1 有丝分裂的阶段
The spindle(纺锤体) and kinetochores(动粒) of chromosomes constitute the mitotic apparatus.
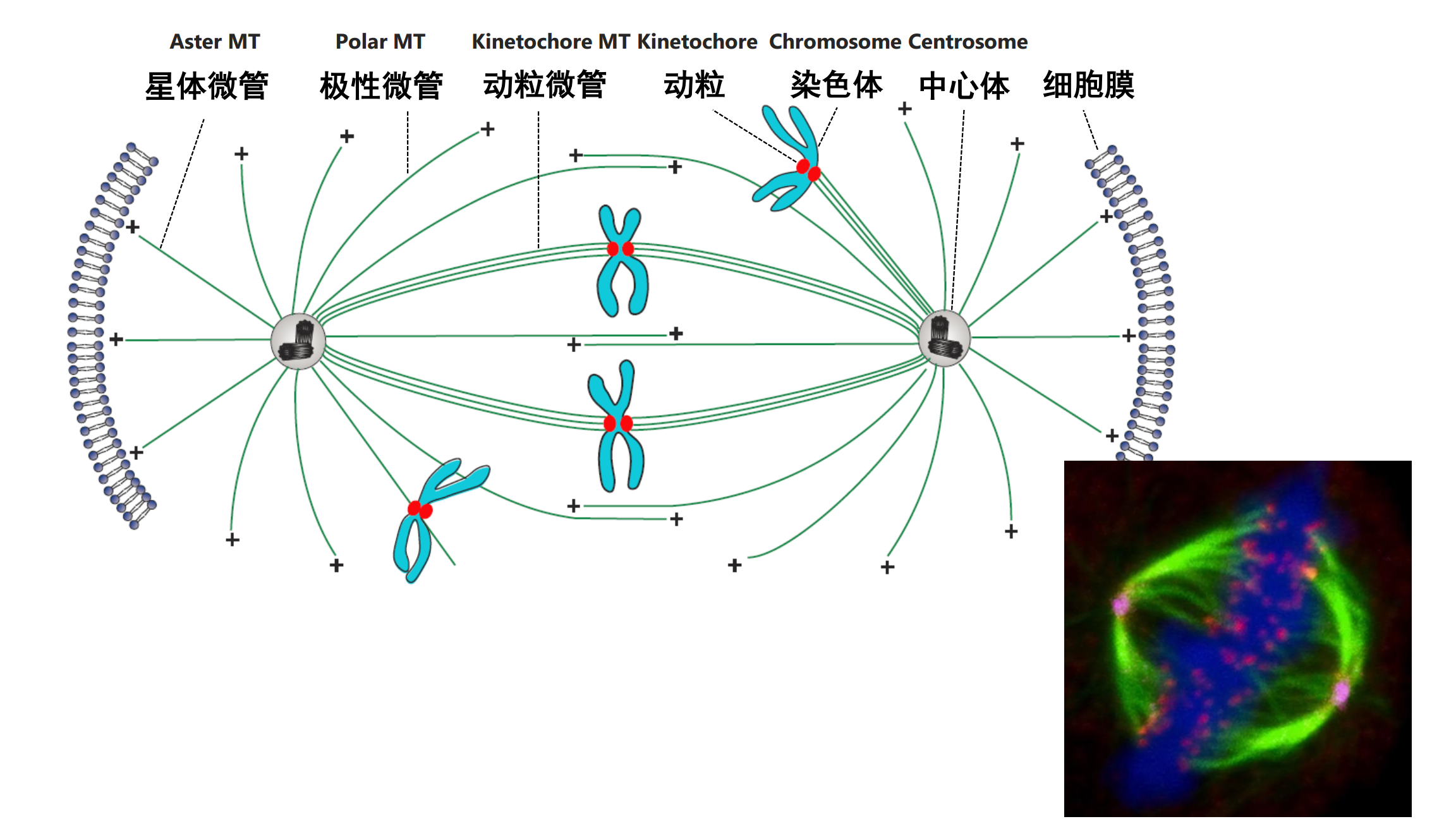 M期可以分为六个阶段:
M期可以分为六个阶段:
- 前期:染色体开始凝聚、纺锤体开始形成、 核膜完整
- 前中期:核膜破裂,染色体未完成排列
- 中期:染色体完全排列在赤道板上
- 后期:染色单体分离
- 末期:染色体解凝聚,核膜重新形成
- 胞质分裂:缢缩环形成至子细胞分离
5.2 spindle 微管
MT-based molecular motors are critical for spindle assembly: kinesin——驱动蛋白; dynein——动力蛋白;
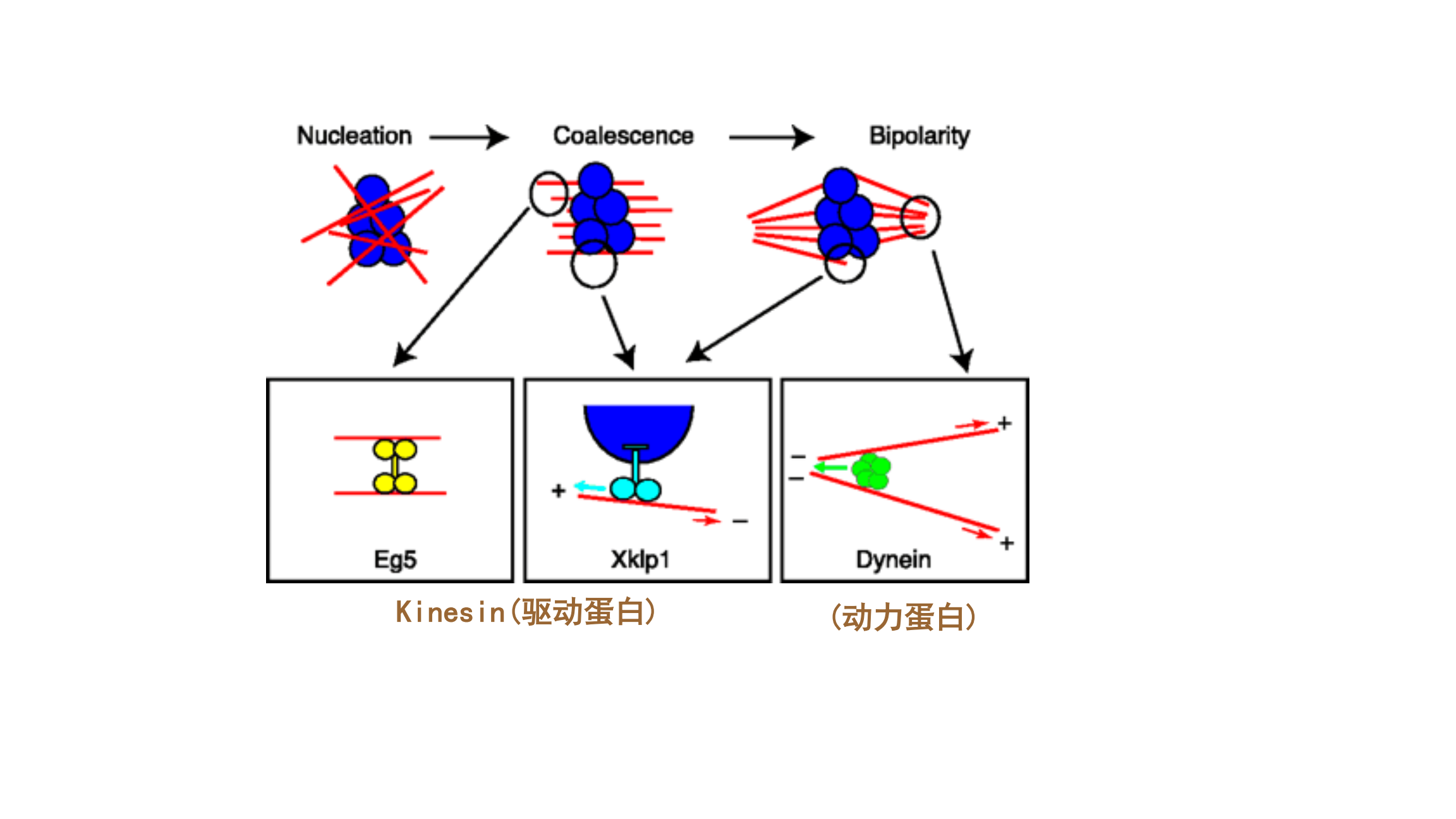
- Vertebrate spindle contains a lamin B-enriched spindle matrix important for spindle formation. 脊椎动物主轴包含富含纤维素B的 纺锤体基质对于纺锤形成很重要.
- Spindle matrix is a supramolecular network formed through protein phase transition. 纺锤体基质是通过蛋白质相变形成的超分子网络.
- Spindle matrix might regulate cell fate.
纺锤体基质可能会调控细胞命运。
- 开放有丝分裂可能通过纺锤体基质调节后生动物细胞命运.
5.3 kinetochore (动粒)
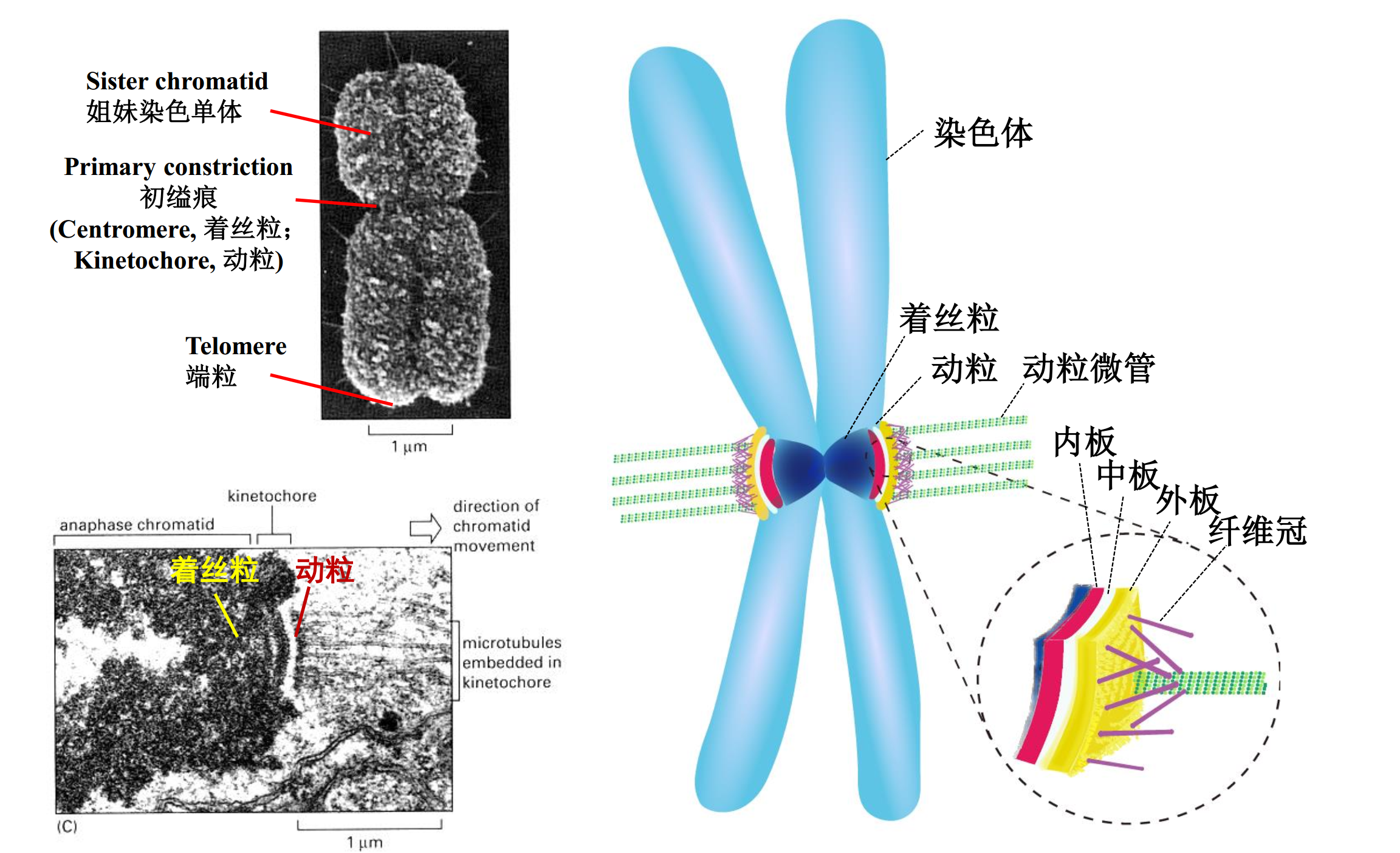
5.4 MT-kinetochore interaction 微管动粒相互作用
分子马达对染色体运动至关重要!!!
- dynein——拉;
- kinesin——推。
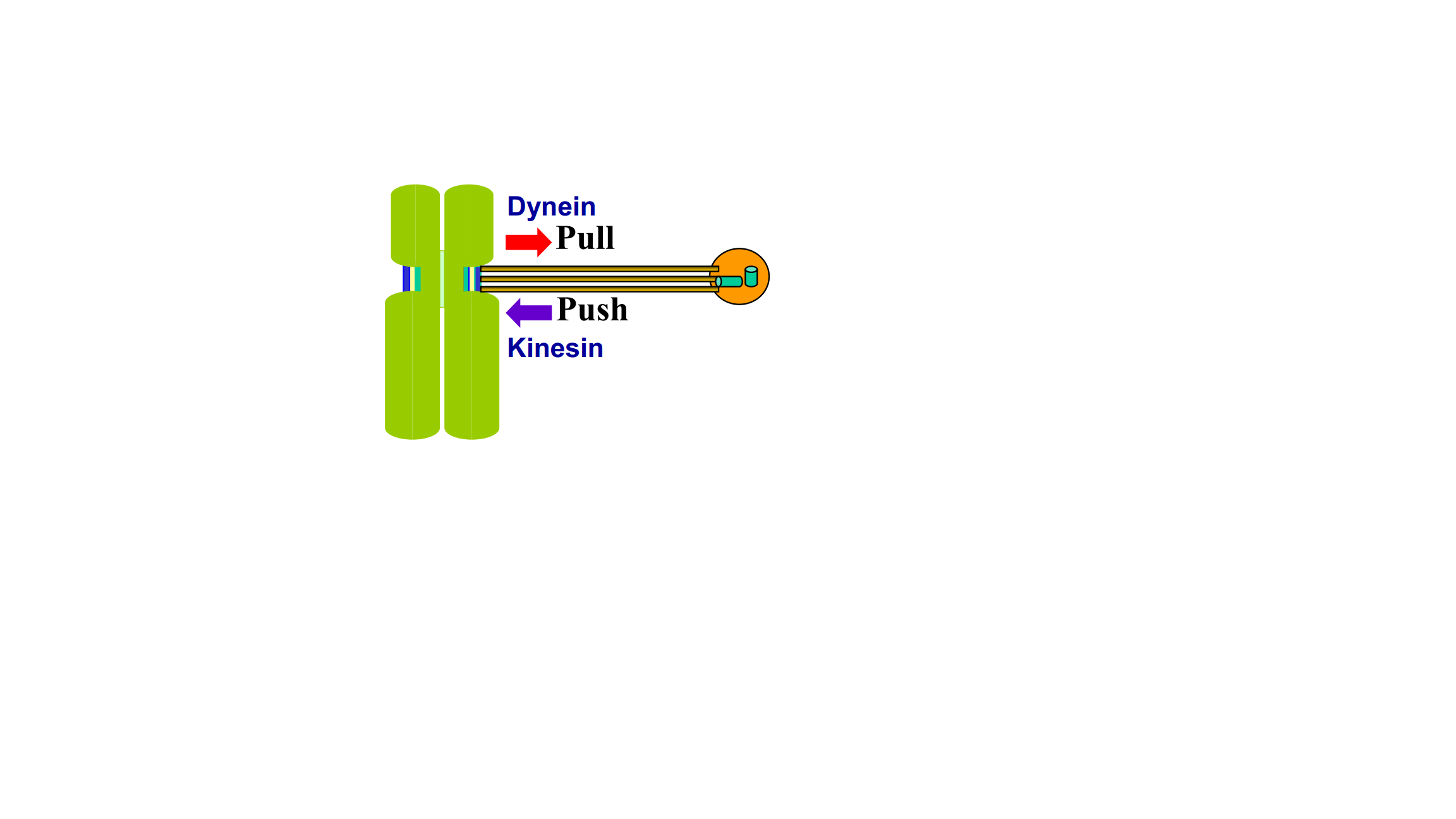 Inactivation of dynein impairs the poleward pulling force on kinetochores / 动力蛋白的失活削弱了动粒上的极向拉力
Inactivation of dynein impairs the poleward pulling force on kinetochores / 动力蛋白的失活削弱了动粒上的极向拉力
Do MTs know which kinetochores to attach?
- Incorrect MT-kinetochore attachments can occur in prometaphase. / 前中期可能会发生错误的微管动粒连接。
- Incorrect MT attachments can be restored.
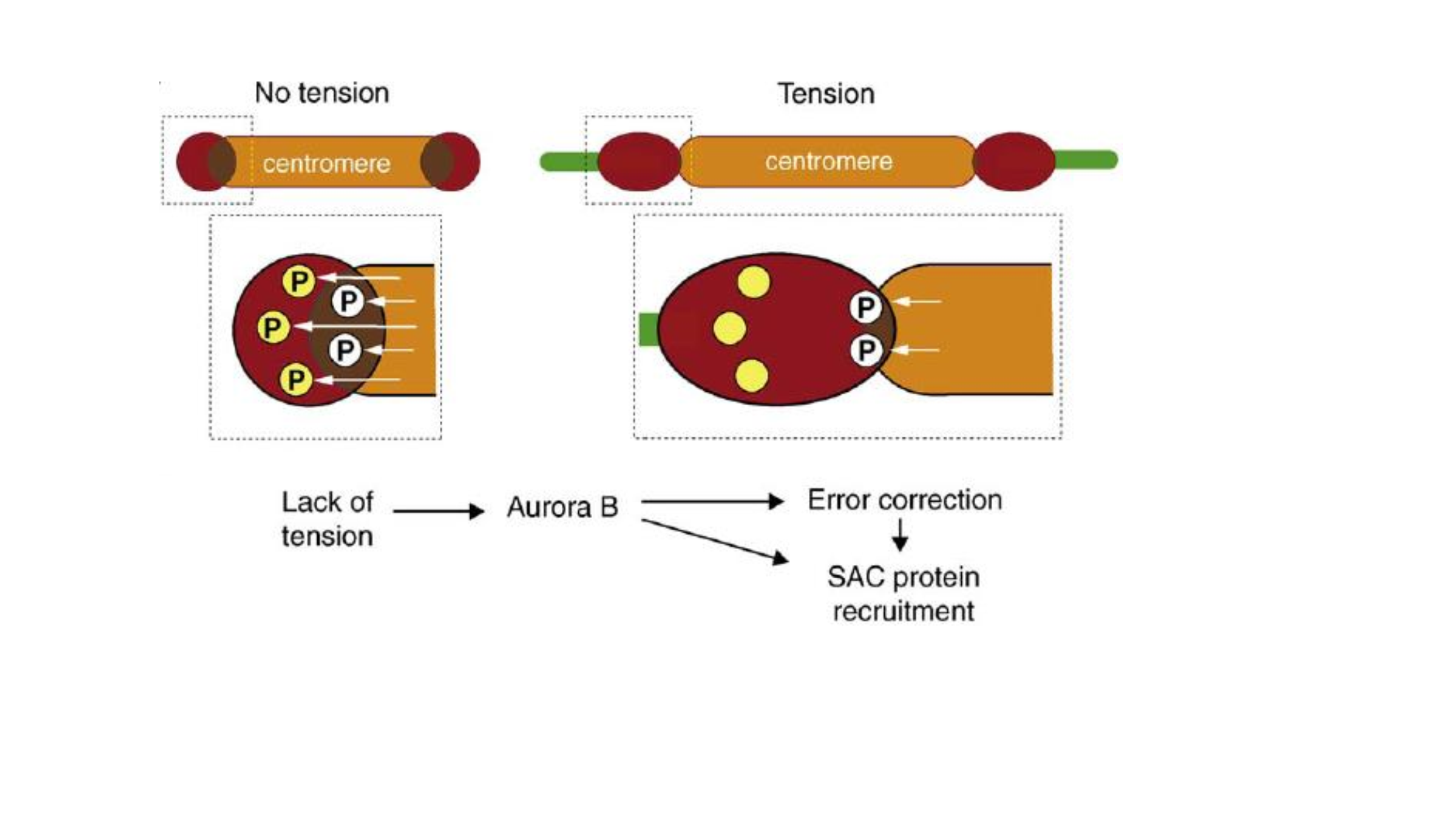
5.5 spindle checkpoint(纺锤体检查点)
- Cells with unattached or misattached chromosomes cannot initiate anaphase unless the spindle checkpoint is compromised.
- The spindle checkpoint guarantees proper anaphase onset.
- A single unattached kinetochore is sufficient to block anaphase onset!!!
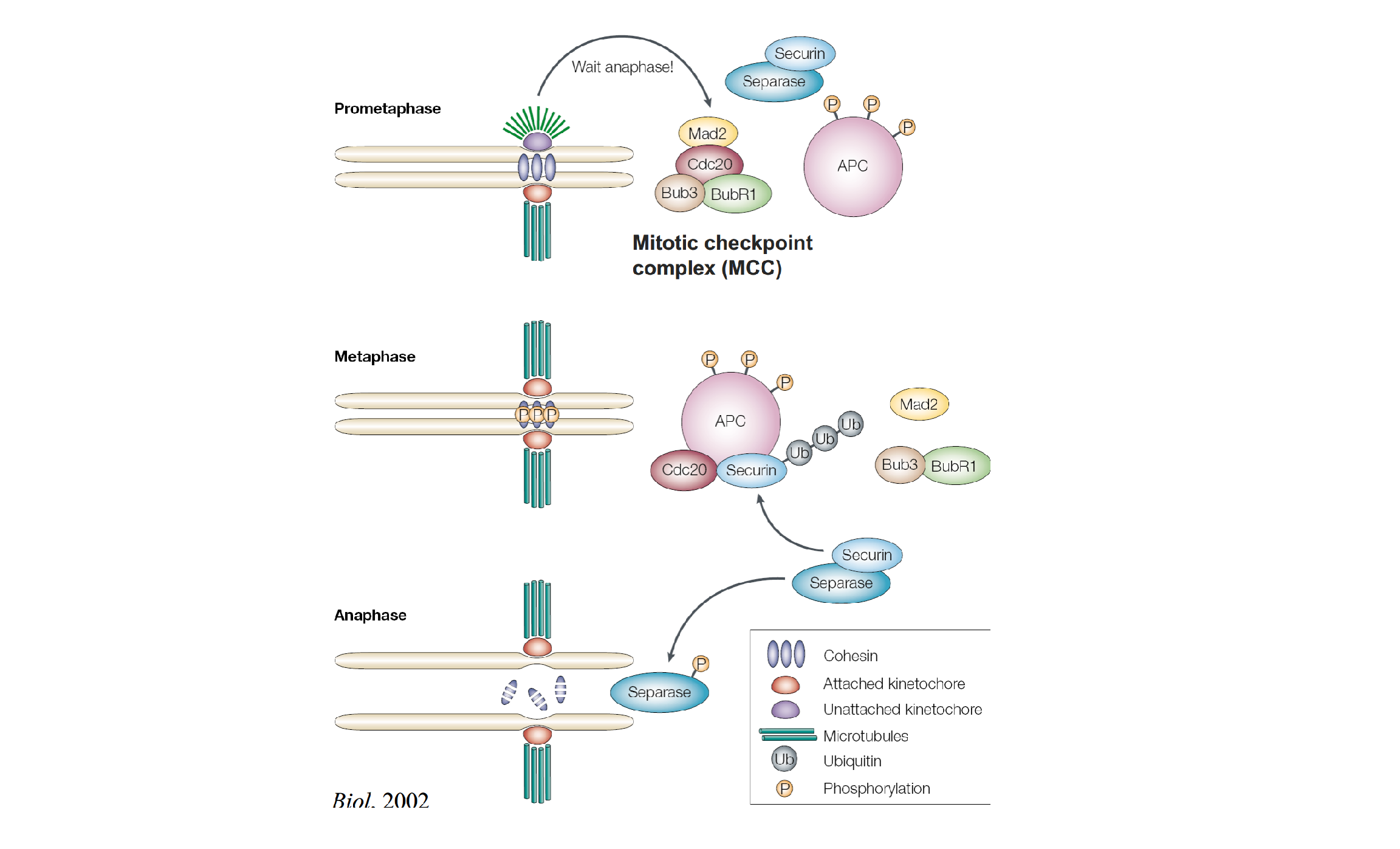 Detailed mechanism of the spindle checkpoint:
Detailed mechanism of the spindle checkpoint:
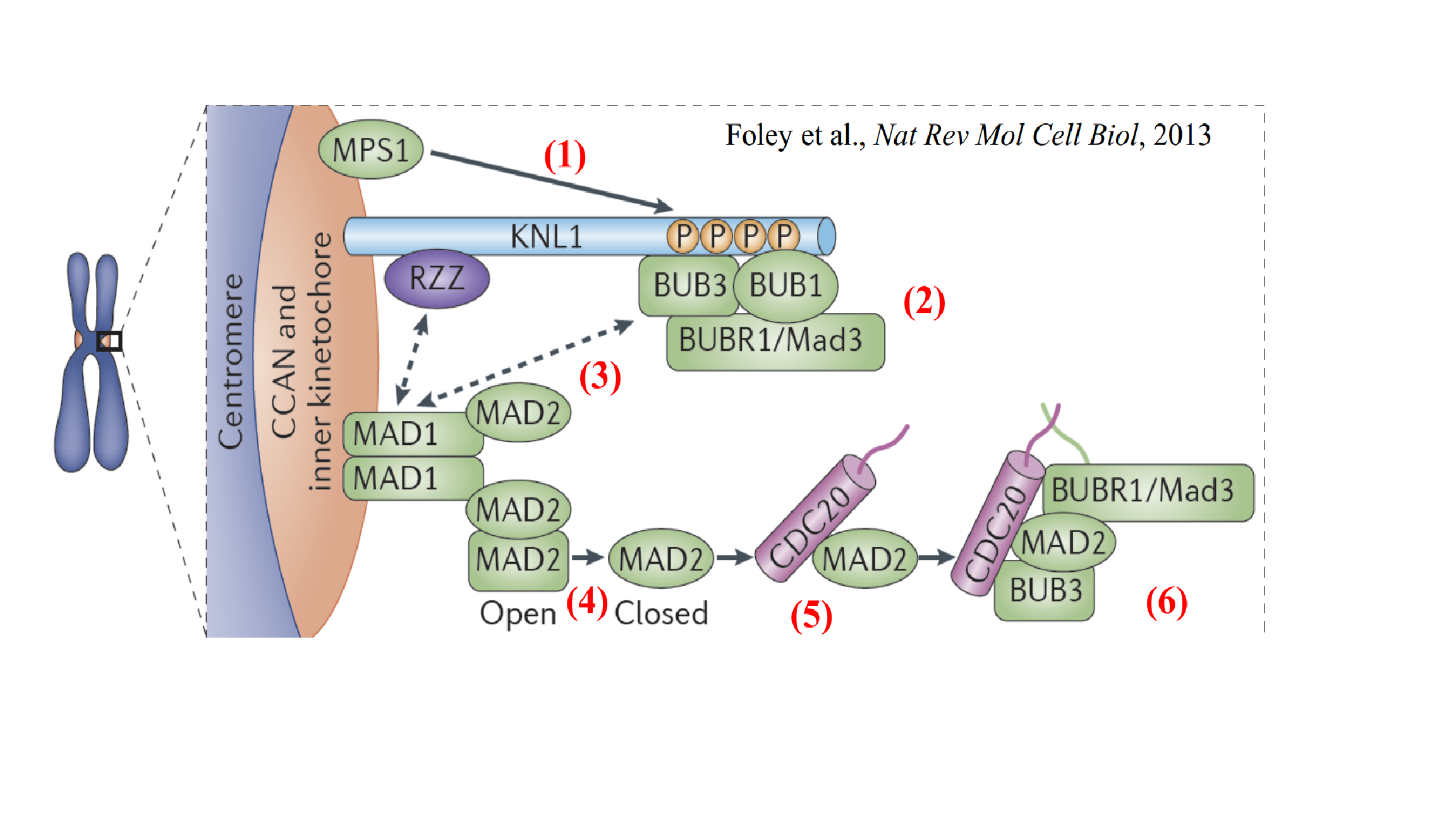 (1) 未结合微管的动粒上MPS1磷酸化KNL1;
(2) 磷酸化KNL1结合Bub1和Bub3,招募BubR1和Mad3;
(3) 上述复合物招募Mad1-Mad2二聚体;
(4) 二聚体将开放状态的Mad2催化为关闭状的Mad2;
(5) 关闭状的Mad2结合Cdc20;
(6) 进一步结合其它检查点蛋白形成MCC。
(1) 未结合微管的动粒上MPS1磷酸化KNL1;
(2) 磷酸化KNL1结合Bub1和Bub3,招募BubR1和Mad3;
(3) 上述复合物招募Mad1-Mad2二聚体;
(4) 二聚体将开放状态的Mad2催化为关闭状的Mad2;
(5) 关闭状的Mad2结合Cdc20;
(6) 进一步结合其它检查点蛋白形成MCC。
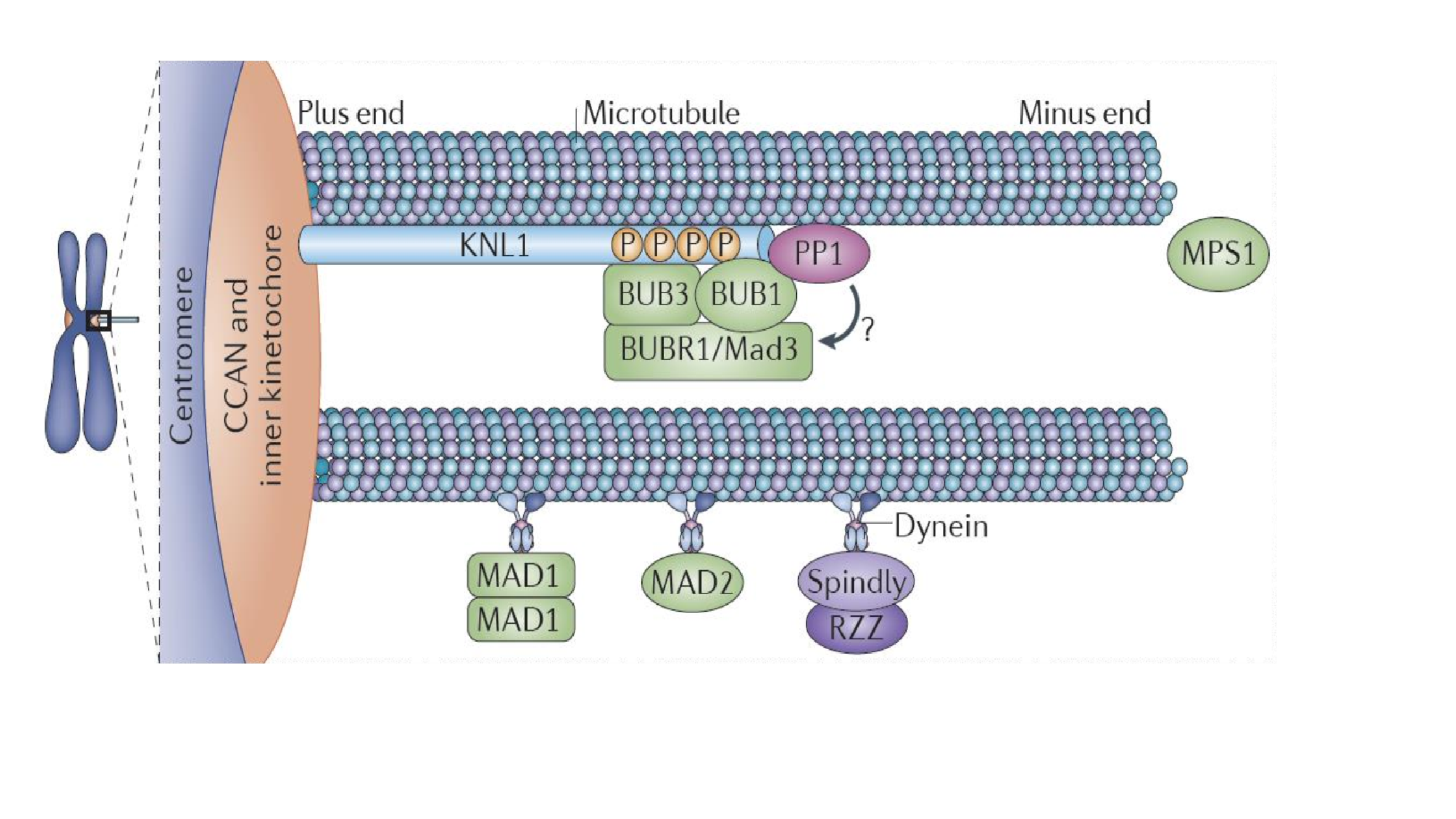 (1) MPS1脱离动粒,使Bub3复合物脱离;
(2) Dynein将其它蛋白质搬离动粒;
(3) 闭合状的Mad2不能产生,对Cdc20的抑制消失;
(4) Cdc20激活APC,降解Securin和Cyclin B。
(5) Securin被降解,激活seperase,从而降解连接姐妹染色单体的cohesin。
###5.6 特殊的细胞分裂
1.Synchronized mitosis in Drosophila embryo.
果蝇胚胎同步有丝分裂。
2.Polarized cell division in epithelia.
上皮细胞中的极化细胞分裂。
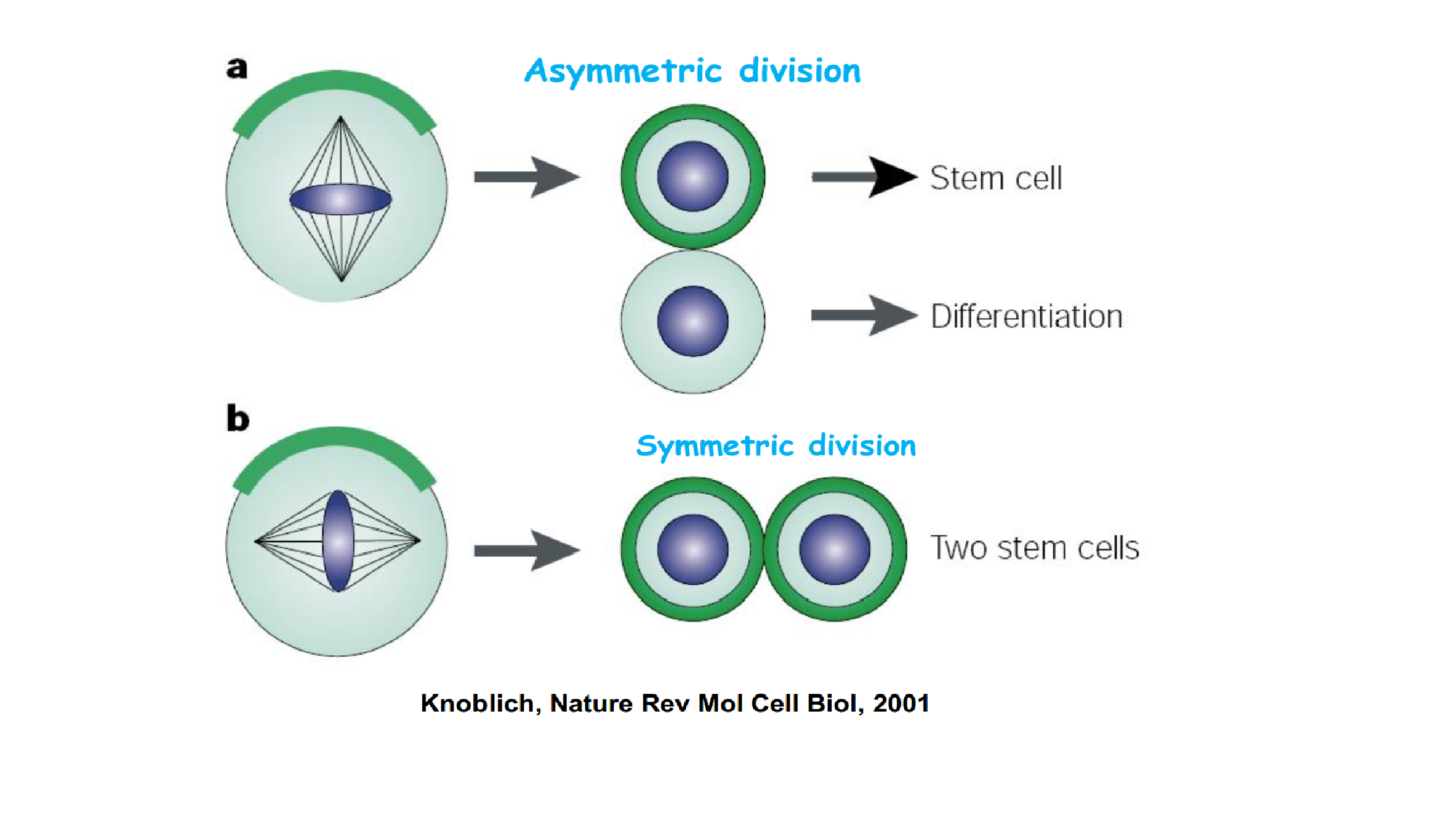
3.Asymmetric cell division of stem cells
干细胞的不对称细胞分裂。
(1) MPS1脱离动粒,使Bub3复合物脱离;
(2) Dynein将其它蛋白质搬离动粒;
(3) 闭合状的Mad2不能产生,对Cdc20的抑制消失;
(4) Cdc20激活APC,降解Securin和Cyclin B。
(5) Securin被降解,激活seperase,从而降解连接姐妹染色单体的cohesin。
###5.6 特殊的细胞分裂
1.Synchronized mitosis in Drosophila embryo.
果蝇胚胎同步有丝分裂。
2.Polarized cell division in epithelia.
上皮细胞中的极化细胞分裂。
3.Asymmetric cell division of stem cells
干细胞的不对称细胞分裂。